CDC’s Findings
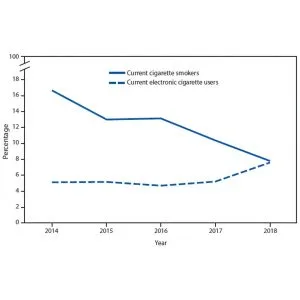
A recent study released by the Centre for Disease Control and Prevention presents intriguing data. The CDC reports that between 2014 and 2018, the percentage of young adults aged 18-24 who currently smoke cigarettes in the United States has dropped from 16.7% to 7.8%. This represents an overall reduction of over 50% in smokers aged 18-24, indicating no ‘gateway effect’ of vaping.
Increase in E-Cigarette Usage
During the same period, the percentage of adults in this group who currently use electronic cigarettes (e-cigarettes) has risen from 5.1% to 7.6%, an increase of 33%.
Debunking the ‘Gateway Effect’
The notion that an increase in the use of e-cigarettes will lead to an increase in adult smokers seems to be unfounded based on this CDC information. In contrast, the number of young adult smokers has seen a significant reduction over the past 5 years.
The Net Result
The overall net result is a 50% decrease in young adults smoking cigarettes, and an overall increase in non-smokers aged 18-24 from 78.2% to 84.6%.